Business Insights
We are often approached by organisations expressing their frustration with the fact that, despite having expensive and leading edge operational and financial systems, they are unable to produce meaningful, unambiguous, consistent and relevant information from such systems.
It is our view that most operational and financial systems are not suited architecturally for reporting purposes and to achieve this goal, the data of an organisation has to be transformed and stored in a consistent and reporting-friendly structure (a data warehouse) from where key business insights can be derived without having to apply further business logic or coding. Therefore, if two individuals in an organisation ask the same question, they should get the same answer, irrespective of the method of seeking the answer from such data warehouse. This is what is meant by having one version of the truth.

Why do you need a Business Insight Solution?
Consolidation of data from multiple systems
Many organisations operate diverse and multiple systems and a data warehouse acts as a simplifying nexus,
hub or consolidation point in the flow of information that eliminates point-to-point integrations between
these systems and group information requirements:


In the figure above we assume that an organisation has say 100 transaction systems and has a requirement for 10 consolidated reports, each report would have to be linked to each of the systems resulting in 1,000 data integration processes.
When a data warehouse is introduced, each of the 100 transaction systems is integrated into the data warehouse and each of the 10 reports is linked to the data warehouse resulting in only 110 data integration processes.
This scenario is very real. At one of our global clients, over 100 transactional systems in more than 50 countries had to be interrogated to answer just one question – What revenues do we derive from our top 10 clients in the region? Due to the manual effort involved, this question could only be answered on a quarterly basis, involving accountants and analysts in 50 countries extracting and summarising data onto spreadsheets that were sent back to head office for collation with no guarantee of the accuracy or completeness of the numbers. However, integrating the data from these systems into a single data warehouse that is updated daily means that this type of question can now be answered daily and within seconds without any manual intervention.
Operational and financial systems are not optimised for reporting of information


Prodinity has the view that many operational and financial systems ‘break apart’ or ‘fragmentise’ transactions in the pursuit of storage minimisation. Users are then forever trying to put these data pieces together to make sense of the data in reports to provide insight to business leaders.
Prodinity automates this process as part of the design of a data warehouse and improves the functionality of its solutions by applying the following rules of design:
1. Using fully descriptive and consistent table and field names to maximise
transparency and understanding.
2. All business rules and transformation logic are applied and codified in the data warehouse which means that reporting tools only have to deal with aggregation of values and visualisation of data. It therefore follows that the data warehouse is reporting or analysis tool agnostic which allows organisations to change these toolsets or use multiple toolsets without requiring changes in the data warehouse.
Extracting value from data
Our clients have achieved excellent returns on their investment in our well-designed Business Insight Solutions. When we engage with clients on new projects, we normally start the discussions off with the following question – What happens if you do nothing? This helps clients to consider and quantify the cost or risk of doing nothing versus the cost of developing and implementing a Business Insight Solution.
Our clients use our solutions to drive gross margin improvement through pricing adjustments, reductions of discounts and reductions of cost of sales.
They also achieve cost reductions in IT through the reduction of legacy systems and efficiency gains in the production of management information.
Our systems also lead to better compliance (e.g. internal, regulatory and Sarbanes Oxley) and management control through the consistent application of business rules and non-compliance alerts.

What does developing a Business Insight Solution entail?
The main stages and processes involved in architecting a Business Insight Solution is illustrated below:
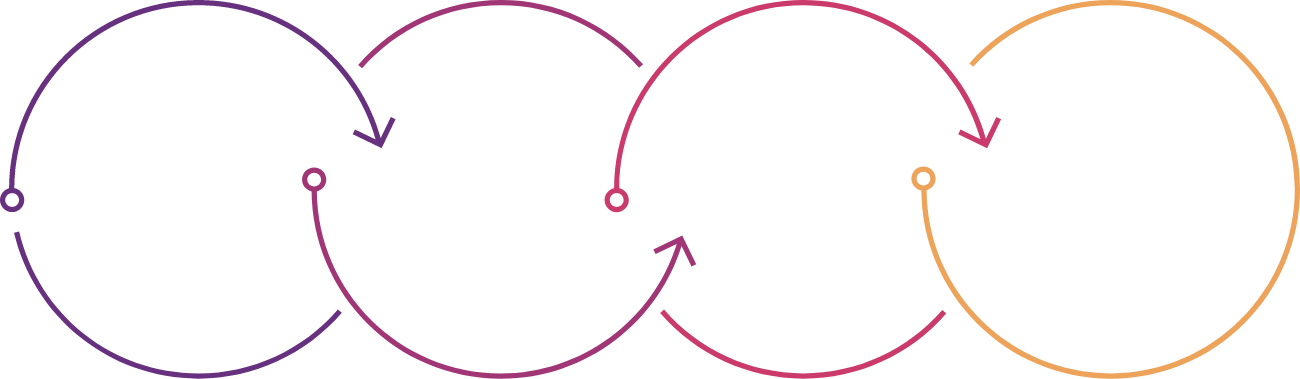
Data Warehouse
Our data warehouse solutions typically have three logical component areas:
Load Area
Required data from operational and financial systems are loaded into tables in the load area and refreshed daily. No data transformation occurs as part of this process which allows for full transparency and an audit trail of source data to reported information. External data used to enrich the data and to aid in master data management is also loaded.
Transformation Area
Here data is transformed and enhanced to fulfil information requirements. The processes involved contain all business rules and logic to render the data fully reportable. The transformation includes system specific processes as well as common processes and application of master data management and enhancement.
Insight Area
This area contains all fully transformed and organised data typically structured into fact and dimension tables that are easily consumable into reporting and data visualisation tools.
We normally build our data warehouse solutions using the Microsoft BI Stack, but if a client has already invested in or has a preference for alternative database technologies
such as Oracle etc., we are able to accommodate this. We are able to design and build our solutions directly within the Microsoft BI Stack or using data warehouse
lifecycle toolsets such as Wherescape Red.
The data warehouse can also be stored ‘on-prem’ on a client’s own IT infrastructure or in the cloud using platforms such as Microsoft Azure or Amazon Web Services (AWS).

Reporting, Data Visualisation and Planning Tools
This is often referred to as the ‘final mile’ delivery of the Insight generation process. The data in the Insight Areas of our data warehouse solutions are reporting and data visualisation tool agnostic. This means that our clients can either continue to use their existing reporting and data visualisation tools or implement alternative ‘best of breed’ toolsets to fit client requirements with no additional coding or data transformation. We have successfully integrated data from our data warehouse solutions into well-known toolsets such as Analysis Services, Business Objects, Olation, Power BI, QlikView and Tableau, to name just a few.
What makes us different?
Prodinity has access to a best-in-class talent pool in the UK and Poland. Our teams have in-depth knowledge of data warehouse design and implementation as well as reporting, data visualisation, planning and budgeting tools and techniques including OLAP, AI, Machine Learning and Data Science.
We understand information requirements and how planning and reporting processes work in organisations. Our consultants have first-hand and extensive experience having worked in financial and IT environments, at operational through to board levels.
As a result, we are ideally positioned to advise you on appropriate solutions and technically experienced to help you through the implementation and training phases of a Business Insight Solution project. Our long-term relationship with clients is also a testimony of our uncompromising and on-going support.
How do we work?
Prodinity understands the financial, operational and reputational risk of embarking on a project and failing to deliver. There are after all numerous horror stories of expensive public and private sector IT projects failing or getting cancelled without any benefit ever derived after several years of development. We endeavour to help de-risk the investment decisions of our clients by:
1. Initial engagement including analysis, workshops and proof of concept development and delivery
2. Project management with regular communication and transparency on progress and time incurred
3. Agile approach with short phases of development and deliverables
4. Handover of effective solution ownership to clients, assisting in testing, documentation, training and ongoing support.